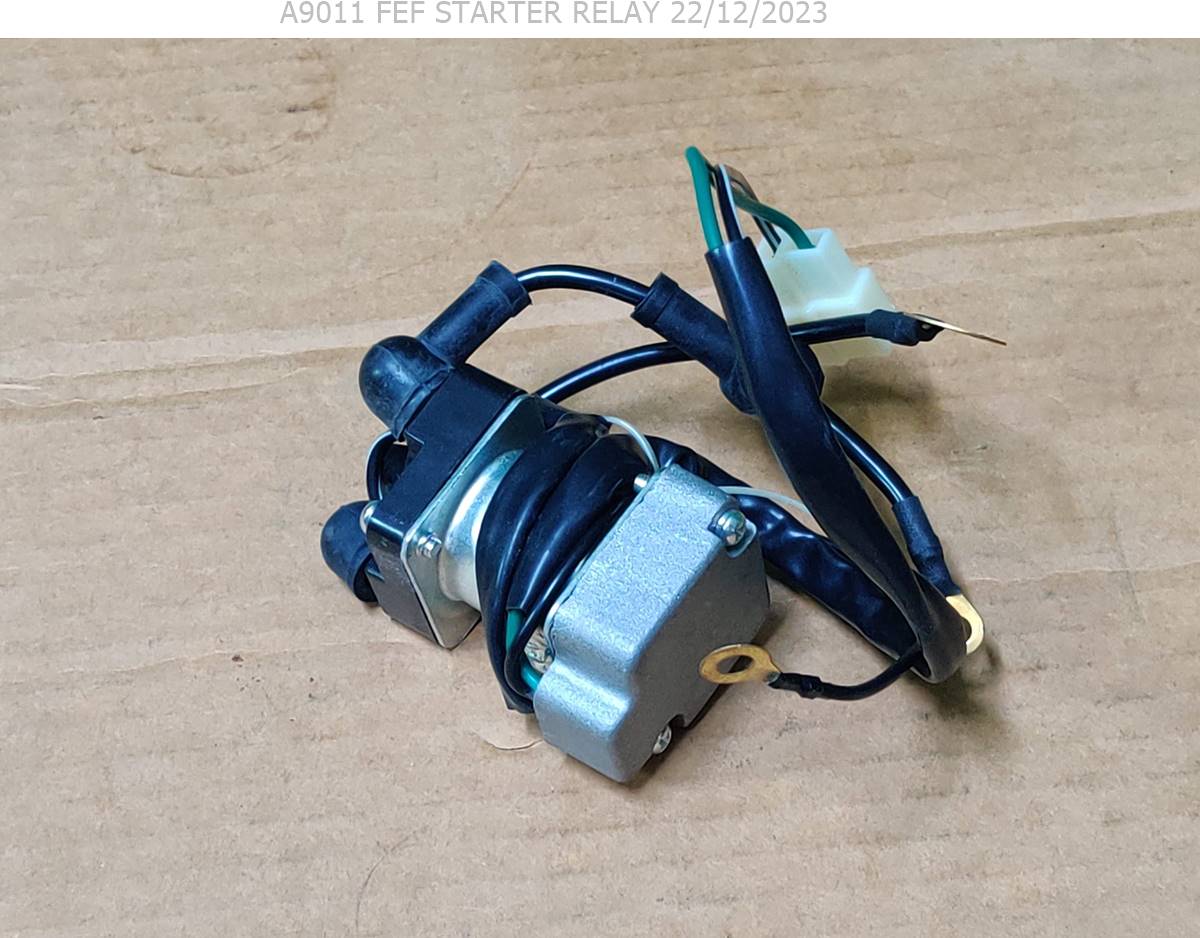
STARTER RELAY
A starter relay, also known as a solenoid, is a crucial component in starting a vehicle’s engine. Here’s how it works:
- Activation: When you turn the ignition key or press the start button, a small amount of current flows through the ignition switch to the starter relay.
- Electromagnetic Coil: Inside the starter relay, there’s an electromagnetic coil. When the current from the ignition switch flows through this coil, it creates a magnetic field around it.
- Contacts: The magnetic field generated by the coil attracts a movable metal contact within the relay, completing an electrical circuit between the battery and the starter motor.
- High Current Flow: Once the circuit is completed, a large amount of electrical current from the vehicle’s battery flows through the relay’s contacts to the starter motor.
- Starter Motor Activation: This high current flow energizes the starter motor, which then cranks the engine, initiating the combustion process and starting the vehicle.
- Release: As soon as you release the ignition key or button, the current flow to the relay’s coil stops. Consequently, the magnetic field dissipates, causing the movable contact to return to its original position, and the circuit between the battery and starter motor is broken.
- Protection: Starter relays often include protective features such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage from electrical faults or excessive current.
Overall, the starter relay serves as a switch that uses a small amount of current to control a much larger current flow, enabling the starting of the vehicle’s engine safely and efficiently.