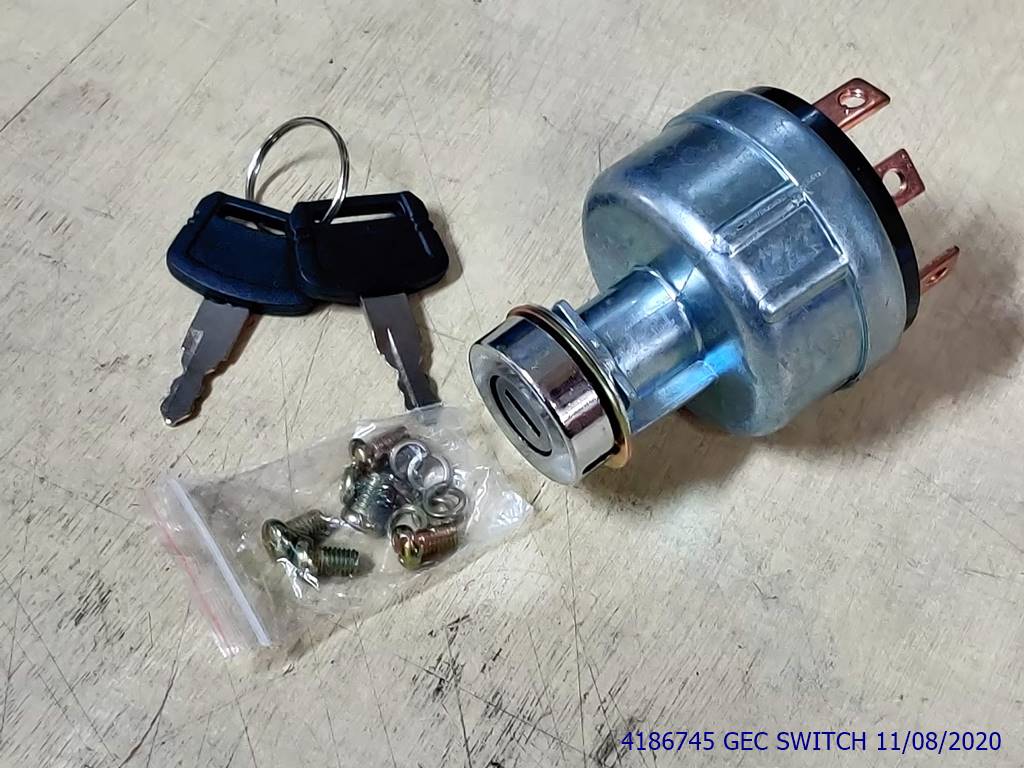
KEY SWITCH
A key switch is a type of electrical switch operated by a physical key. It typically consists of several components:
Key: The physical key is inserted into the switch to activate it. Keys are uniquely shaped to fit into specific switches.
Lock Cylinder: This is the part of the switch where the key is inserted. The lock cylinder holds the key in place and ensures that it can only be turned in specific ways.
Tumblers or Pins: Inside the lock cylinder, there are tumblers or pins that align along a shear line. When the correct key is inserted, the tumblers align at the shear line, allowing the key to turn.
Contacts: When the key is turned, it engages contacts inside the switch, completing or interrupting an electrical circuit. This action can either allow or prevent the flow of electricity to a connected device or system.
Spring: There is usually a spring mechanism inside the switch that returns the key to its original position once it’s released, ensuring that the switch returns to its default state.
Housing: The housing is the outer casing of the key switch, which encloses all the internal components and provides protection and support.
When the correct key is inserted and turned, the tumblers align, allowing the key to turn freely. This action engages the contacts inside the switch, completing the circuit and activating the connected device or system. When the key is turned back to its original position or removed, the contacts disengage, breaking the circuit and deactivating the device or system.